Types of machines and how to maintenance
Machinery, what is it and how many types ?
Machinery is equipment or tools used to process materials or perform various tasks. It often involves the use of energy or electricity for operation. Machinery can be divided into various types based on their usage patterns or intended purposes. Some machinery is used to process materials to create products, such as cutting, drilling, milling, and welding machines. Meanwhile, other types of machinery are used for transportation or travel, such as trains, airplanes, and ships.”
Type of Macinery
Machinery comes in various types and serves different purposes. It is often categorized based on usage patterns in the workplace. For example, for less complex tasks, machinery like hoists, pulleys, and small gears may be used. As the complexity of tasks increases, machinery that operates through computer systems, such as PLC-based machinery, motor-type machinery, and hydraulic-type machinery, becomes more common. Here are examples of machinery in each category:
- Drilling Machines: Used for drilling holes in materials such as metal, wood, or plastic.
- Milling Machines: Used for cutting materials to achieve desired shapes.
- Lathes: Used for rotating materials to achieve desired shapes.
- Turning Machines: Used for removing material from a workpiece by rotating the machine.
- Presses: Used for compressing materials together, such as metal rings.
- Agricultural Machinery: Used as aids in agricultural work, such as tractors, harvesters, and various processing machines.
- Multipurpose Machines: Capable of performing multiple functions in one machine, such as milling and drilling functionalities combined.
Machine CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are machines controlled by computer systems to manage their operations. CNC machines can work with precision and speed compared to manually controlled machines. They are often preferred for tasks requiring high precision, such as cutting, drilling, and milling. Additionally, they can significantly improve efficiency, production quality, and reduce manufacturing losses.
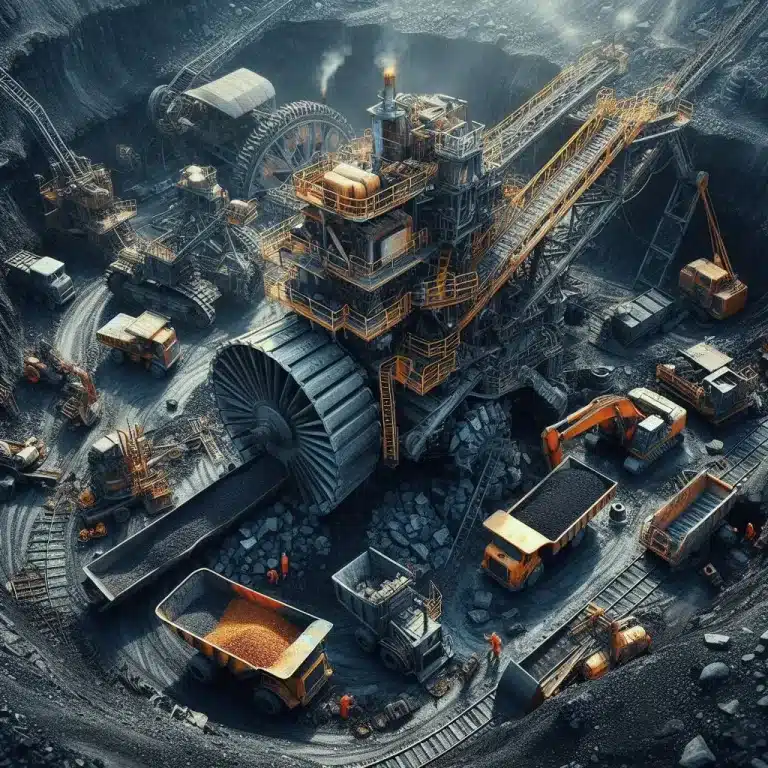




Mining machinery
Mining machinery is equipment or devices used in the mining industry for the extraction and extraction of materials, predominantly ores and rocks. The use of machinery in the mining industry is often associated with tasks such as drilling, excavation, material transportation, crushing or grinding, and material sorting. These machines may include specialized equipment designed specifically for these tasks, as well as machinery used in other related industries. Some types of machinery used in the mining industry include ore drilling machines, ore sizing machines, and ore cleaning machines. These machines are often large and robust to withstand harsh environments in mining operations.
Machine Maintenance
Each type of tool or machinery requires regular maintenance and periodic inspections to ensure they are in a ready-to-use condition. Maintenance of machinery typically requires a team with specific expertise, especially for complex machinery, although even general machinery requires regular upkeep. Prioritizing maintenance of equipment and machinery helps extend their lifespan and reduces the risk of serious consequences, such as personnel injury or work stoppage,Breakdown Maintenance
Machine Maintenance:
- Inspection: It is essential to inspect the condition of the machinery before each use, looking for abnormalities such as unusual noises, vibrations, or leaks.
- Cleaning: Clean the machinery after each use, removing oil residues, dust, and debris.
- Lubrication: Lubricate various parts of the machinery at specified intervals to ensure smooth operation.
- Oil Level Check: Regularly check the oil levels of the engine, hydraulic oil, and other lubricants.
- Part Replacement: Replace damaged or worn-out parts as necessary to maintain optimal performance.
- Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments to the machinery to ensure proper functioning.
- Documentation: Keep records of inspections, repairs, and part replacements.
Types of Maintenance:
- Preventive Maintenance: Conducting maintenance at scheduled intervals to prevent potential issues from occurring.
- Corrective Maintenance: Performing maintenance when machinery experiences a problem or failure.
- Condition-based Maintenance: Carrying out maintenance based on the condition of the equipment and its usage.
Planned Maintenance
Pre-documented and scheduled planned maintenance The purpose of planned maintenance is Reduce machine downtime by requiring rigorous planning and timelines. In the work schedule, it must be clear that Which parts will break and should be replaced periodically. such as replacing shaft bearings And which parts will be maintained at the scheduled time. through preventive maintenance
Zero Breakdown has the main prevention factors divided into 2 major topics: Autonomous Maintenance and Planned Maintenance, and the types of maintenance according to the Planned Maintenance program can be divided as follows.
PM : Preventive Maintenance : It is to maintain the machine must comply with the basic operating conditions of the machine, meaning that it must have normal operation.
DM : Daily Maintenance : Is the maintenance of the machine, also known as daily maintenance, such as lubrication, tightening, adjustment, inspection and replacement of various parts. to measure deterioration
BM : Breakdown Maintenance : It is a repair when the machine is broken. That is not planned in advance and often causes high costs.
TBM : Time Based Maintenance : It is a maintenance that is performed at scheduled intervals at regular intervals.
CBM : Condition Based Maintenance : It is a maintenance form that determines the deterioration of machine parts. using machine diagnostic techniques Then predict the trend according to the probability of deterioration.
PdM : Predictive Maintenance : It is a maintenance that uses new methods or techniques. by using various measuring tools to monitor the machine condition and use that information for maintenance planning.
Run to Failure (RTF) Is part of the Planned Maintenance method, Run to Fail is a strategy that intends to allow equipment or parts to work until they fail or become unusable. And the owner or the maintenance department is ready to fix it immediately or replace it immediately. as planned and prepared spare parts
Technology for predictive maintenance
Oil And Lubrication Solutions
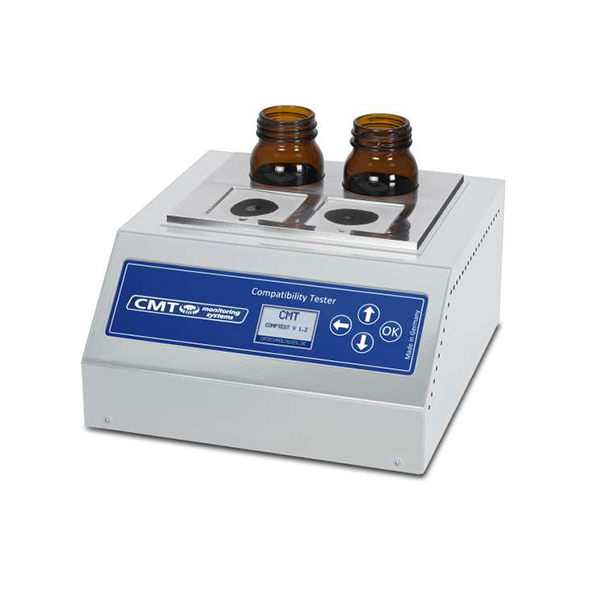
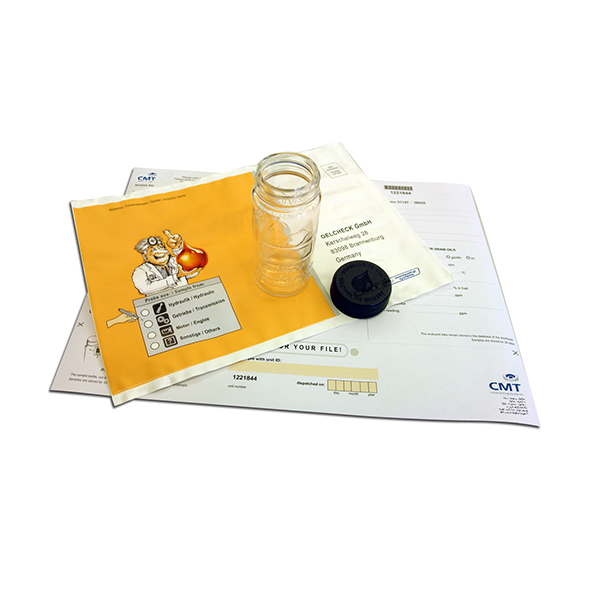
CMT’s oil test kit range offers lubricated machine operators a quick and easy way to self-check their machines at an affordable price. Oil test kits allow you to use the oil test results you get in minutes to make decisions about repairing a particular machine. It helps to confirm whether this critical machine will continue to operate or whether repairs should be planned to prevent unwanted shutdowns. Use your knowledge of oil parameters to understand the condition of your equipment. Choose to use the oil test kit and the parameters you want to know. It can be used separately or together in a single test
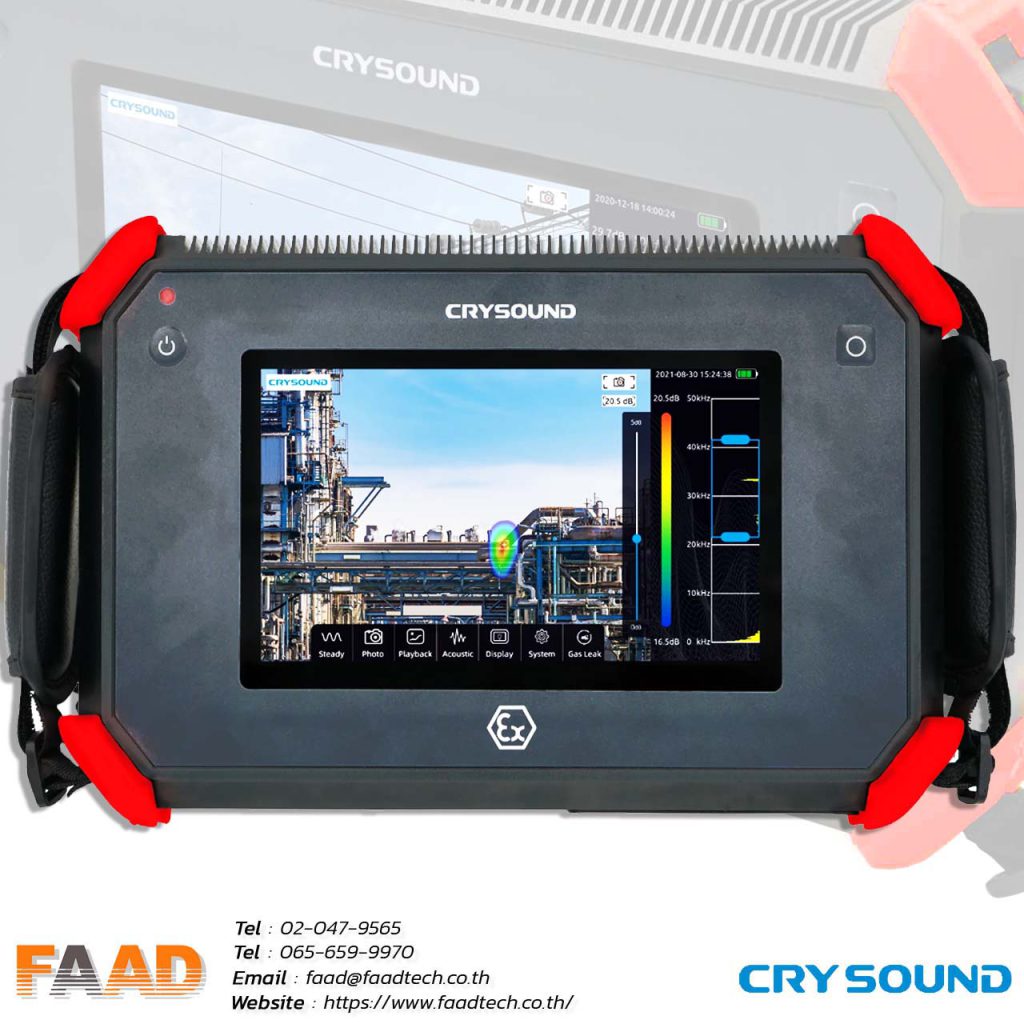
Leak Detector Acoustic Imager | Cry Sound CRY2624 is an explosion-proof instrument suitable for petrochemical and heavy-duty industries.
Analytics and Reports
Template-based processing and recording of data, waveforms,spectra,spectrograms is supported by CRYSOUND report analysis tool software, generating ISO 50001 compliant, editable protocols in Excel format.
PD Detection & PD Type Identification
Partial discharges can be detected before more serious faults would occur, even before a thermal camera would detect them.
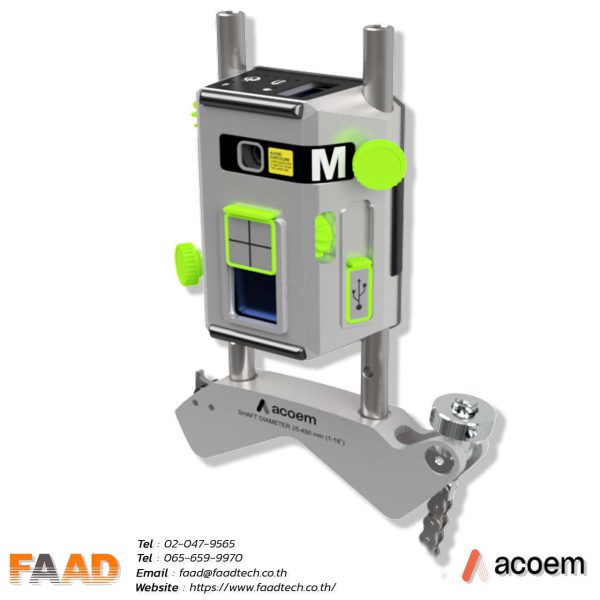
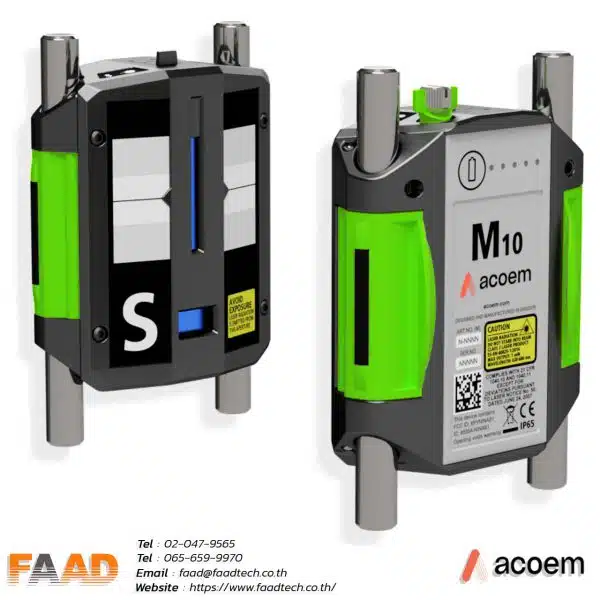
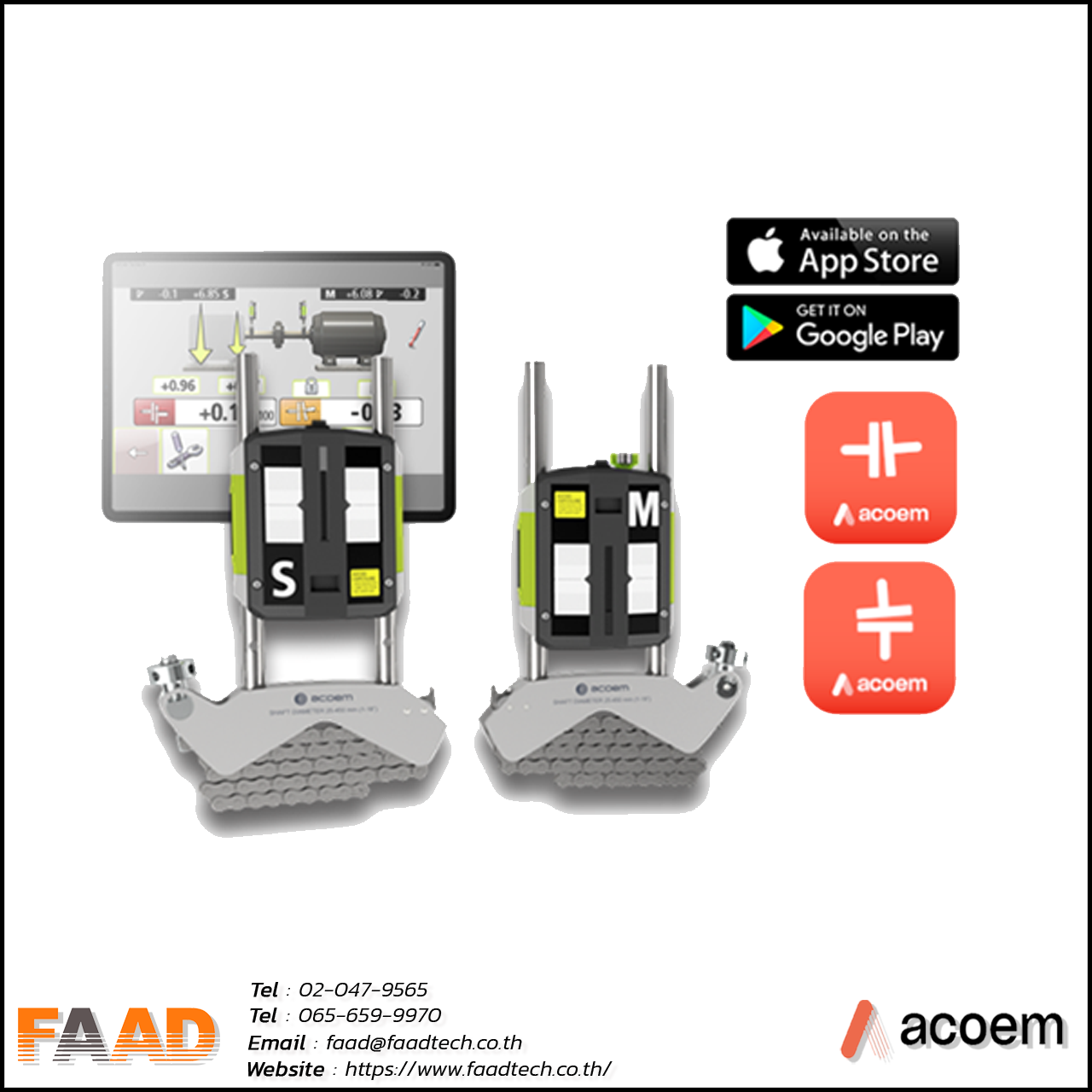
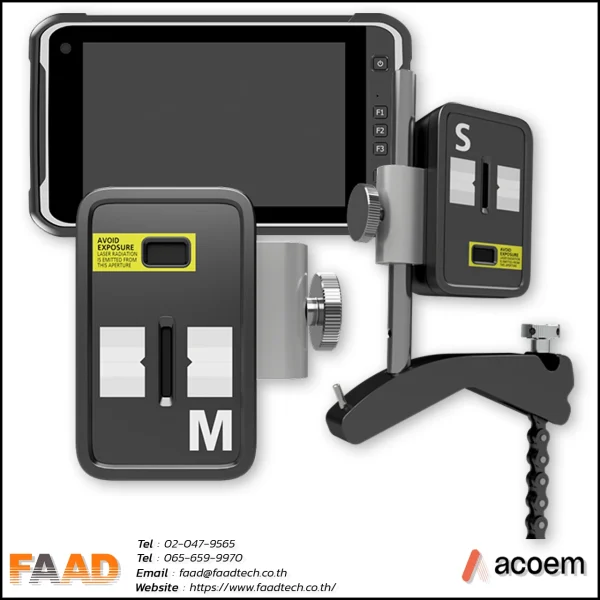
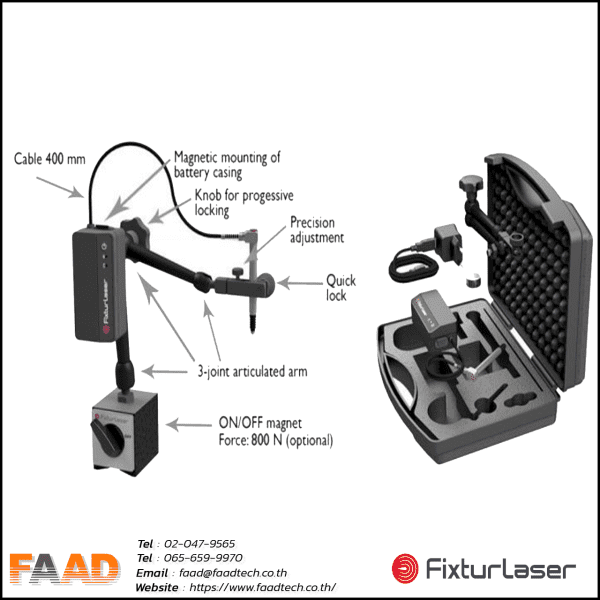
Laser shaft alignment AT400
Innovative 2-axis shaft alignment tool that will create a new standard of precision and efficiency For various shaft alignment applications
- Increase power and enhance standards Productivity and efficiency with advanced sensors and precise 2-axis measurement deliver accurate results.
- Intuitive interface that is easy for ordinary users to understand. Increase the experience for users more satisfied
- Introducing the thinnest 2-axis sensor on the market, weighing 306 grams with a measuring range of 20 meters, revolutionizing high-precision applications.
The large sensing boost sensor measures 20×20 mm and has a high resolution of 0.001 mm, making it suitable for precise position sensing and various measurement applications.
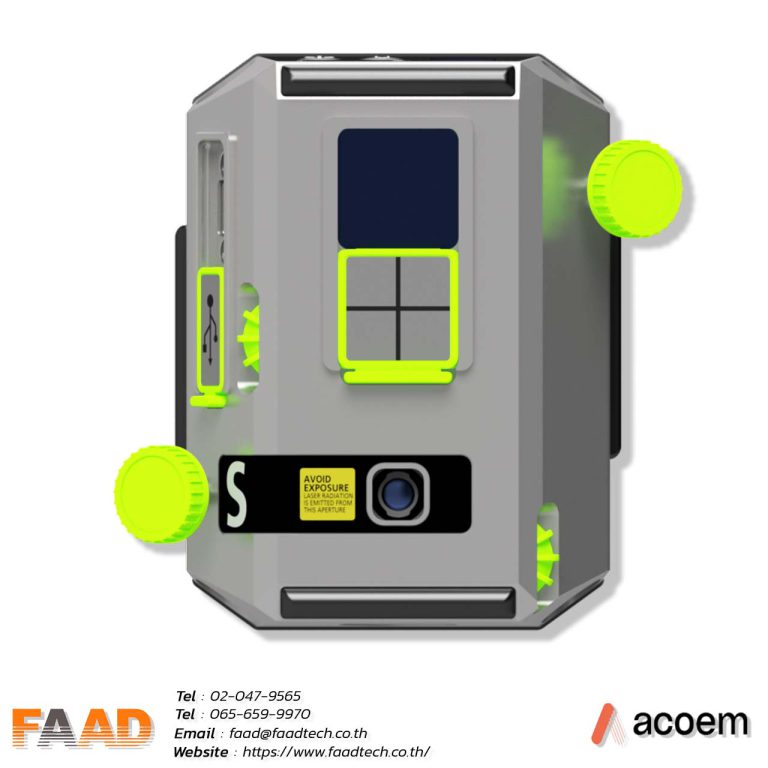
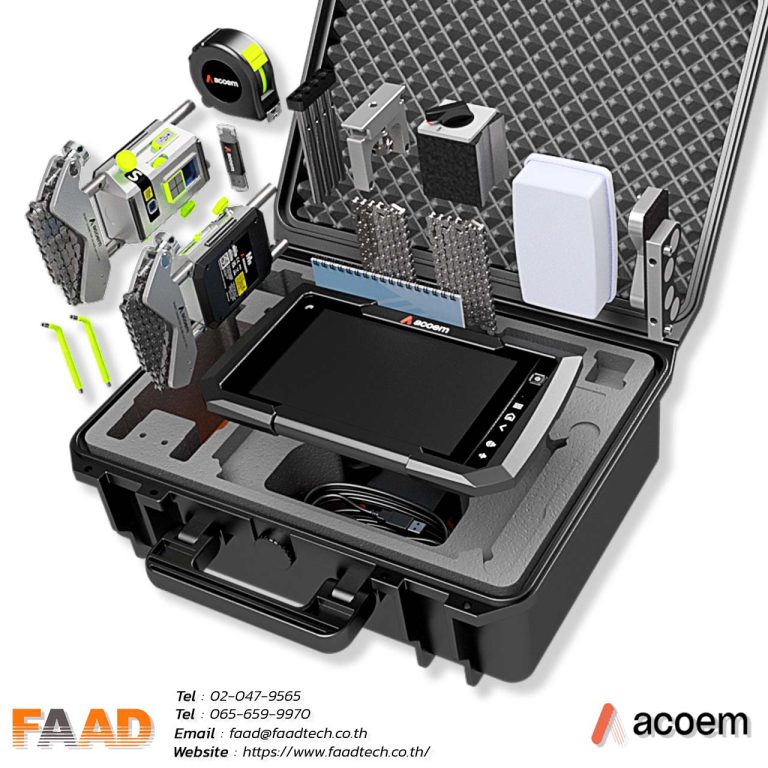
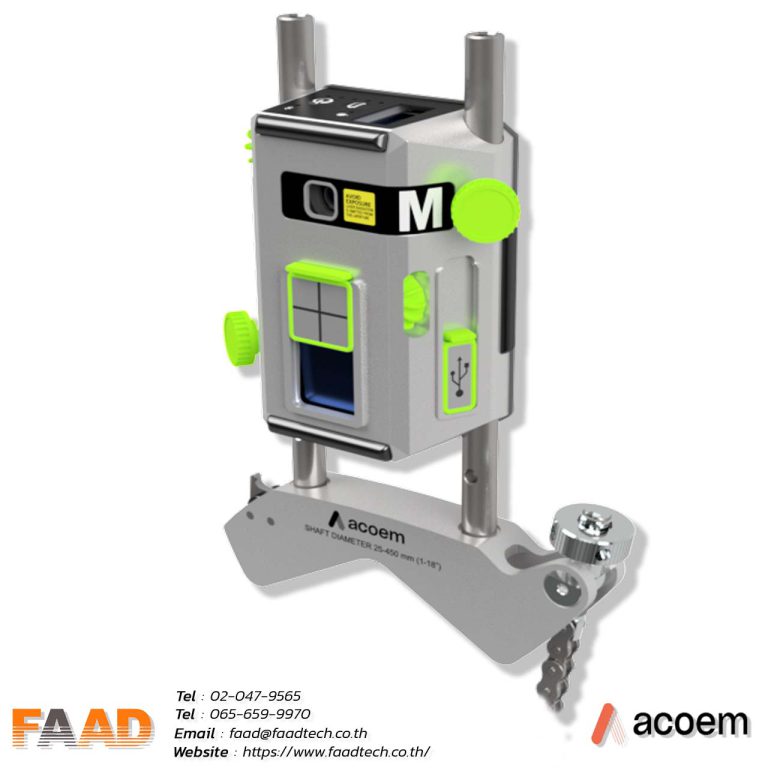



ACOEM : Laser shaft alignment AT400













Read Our Latest News
News & Articles
- By Admin Faadtech
- Comments are off for this post.
- By Admin Faadtech
- Comments are off for this post.